What’s the difference between a cruise missile and a ballistic missile?
- By Alex Hollings
Share This Article
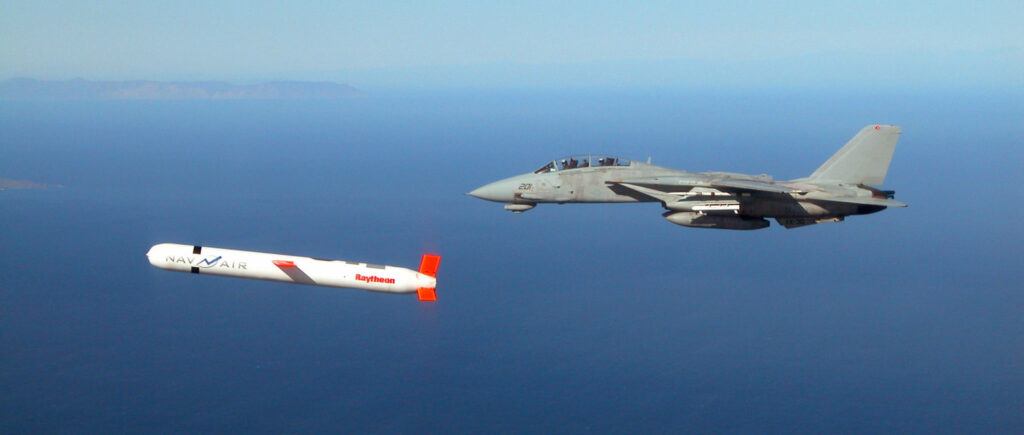

It’s not at all uncommon to see news stories featuring discussions about missile platforms and their capabilities, from Darpa’s recent test of a hypersonic cruise missile to discussions about the destructive power of Russia’s latest intercontinental ballistic missile, the RS-28 Sarmat. As a result, you may have found yourself wondering… what exactly is the difference between a ballistic missile and a cruise missile?
In the interest of brevity, you can really sum up the difference between these types of weapons with the trajectory that they follow. A ballistic missile follows a “ballistic flight path,” which often includes traveling along a long arc, whereas a cruise missile tends to follow a straighter, lower altitude trajectory. Another easy (if not exactly precise) way to think about them is that ballistic missiles are more like rockets, while cruise missiles are more like aircraft or drones.
Ballistic missile basics
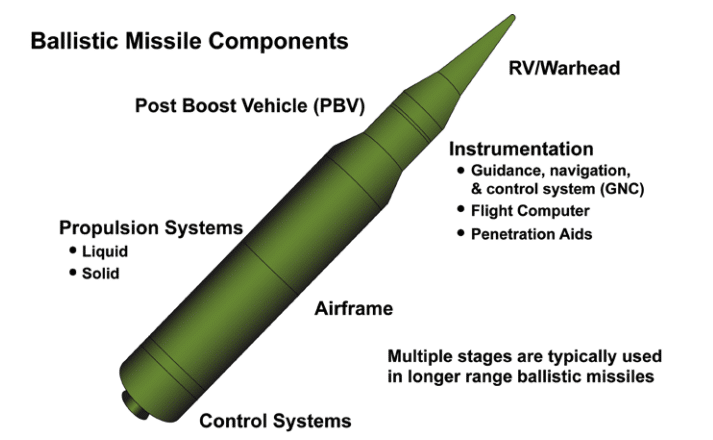
While both ballistic and cruise missiles can carry nuclear payloads, the most commonly understood (and feared) nuclear weapon delivery vehicle of the modern era falls under the ballistic category: the ICBM. And while there are many variations in the employment of different sorts of ballistic missiles, the ICBM model offers a simple way to appreciate the concept behind a “ballistic flight path.”
A ballistic missile is propelled into the air by a rocket motor, or often (as is the case with ICBMs) multiple staged rocket motors. ICBMs bear a striking resemblance to the rockets that take astronauts into space for good reason, other than the payloads these platforms carry, they are mechanically very similar.
Related: What exactly is America’s nuclear triad?
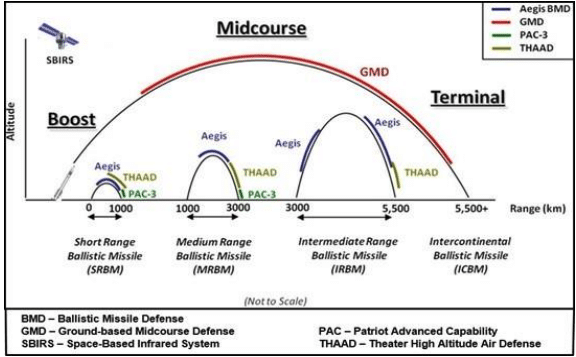
These rocket motors carry the ballistic missile to a high altitude (boost phase) until the rocket fuel is entirely expended. At that point, known as the midcourse phase, the missile reaches its highest altitude before it begins to travel back down its arced flight path. For ICBMs, this phase can last up to 20 minutes, with the missile itself traveling at speeds of around 15,000 miles per hour.
It then begins its unpowered descent, known as the terminal phase, traveling at speeds of nearly 2,000 miles per hour until it collides with its target.
Related: How do America’s nuclear submarines get resupplied at sea?
Cruise missile basics

Unlike the long arcing trajectory of a ballistic missile, a cruise missile travels at lower altitudes and on far straighter trajectories. In fact, it might be easiest to think of a cruise missile as a drone of sorts that flies on its own to its intended target and then proceeds to crash into it. Perhaps the most commonly discussed cruise missile in modern use is the Tomahawk, which has become America’s weapon of choice for engaging targets at fairly long distances without deploying troops to a conflict.

Cruise missiles don’t leave the atmosphere at any point during their flight, nor do they travel unpowered for any significant duration. Rather than rocket engines, cruise missiles are powered by turbofans just like many tactical aircraft, and most often, even have wings that deploy after they’ve launched. Some cruise missiles can even be guided into their target by remote operators using cameras on the weapon’s nose, again, not unlike piloting a drone or UAV.
Modern cruise missiles are known for their range and excellent accuracy. In fact, the common rule of thumb regarding these weapons is, “It can fly 1,000 miles and hit a target the size of a single-car garage.”
Read more from Sandboxx News:
- 3 training basics every soldier needs to remember
- How do America’s nuclear submarines get resupplied at sea?
- A missile race is heating up all across Asia
- America’s plan to build 747 arsenal ships packed with cruise missiles
- America really launched an ICBM from the back of a C-5 cargo plane
Feature image: U.S. Navy
Related Posts
Sandboxx News Merch
-

‘AirPower’ Classic Hoodie
$46.00 – $48.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

‘Sandboxx News’ Trucker Cap
$27.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

‘Kinetic Diplomacy’ Bumper Sticker (White)
$8.00 Add to cart

Alex Hollings
Alex Hollings is a writer, dad, and Marine veteran.
Related to: Airpower
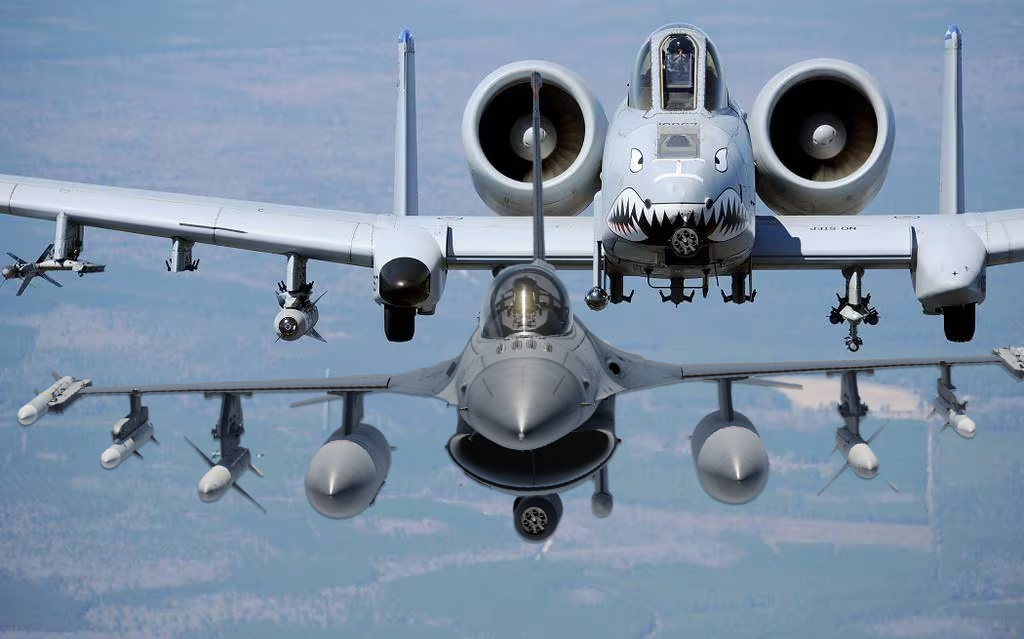

F-16s carrying the A-10’s 30mm cannon actually saw combat
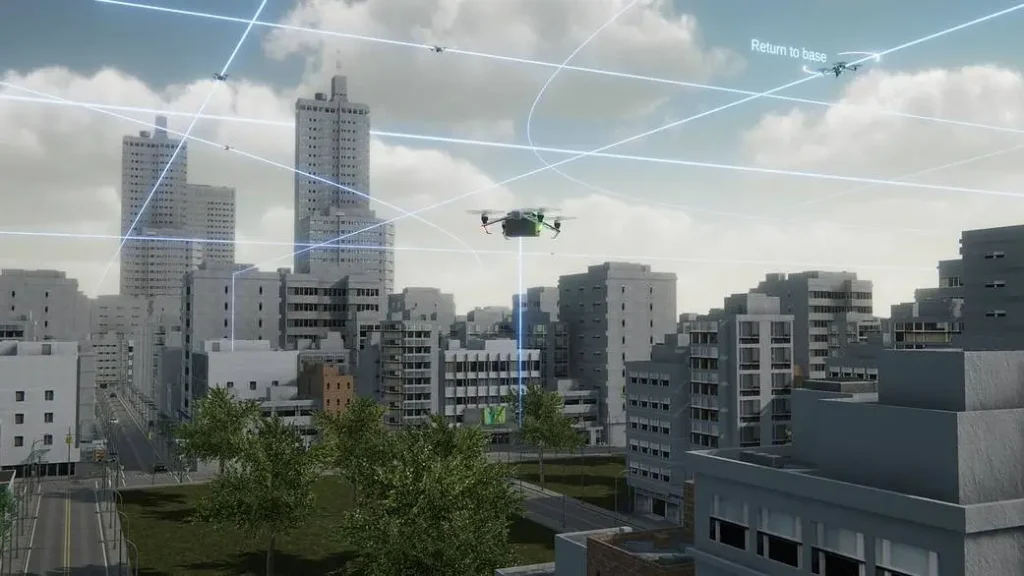

Drone mystery solved? This little-known government program may explain New Jersey’s drone sightings

How American Abrams tanks devastated Russian tanks in Iraq
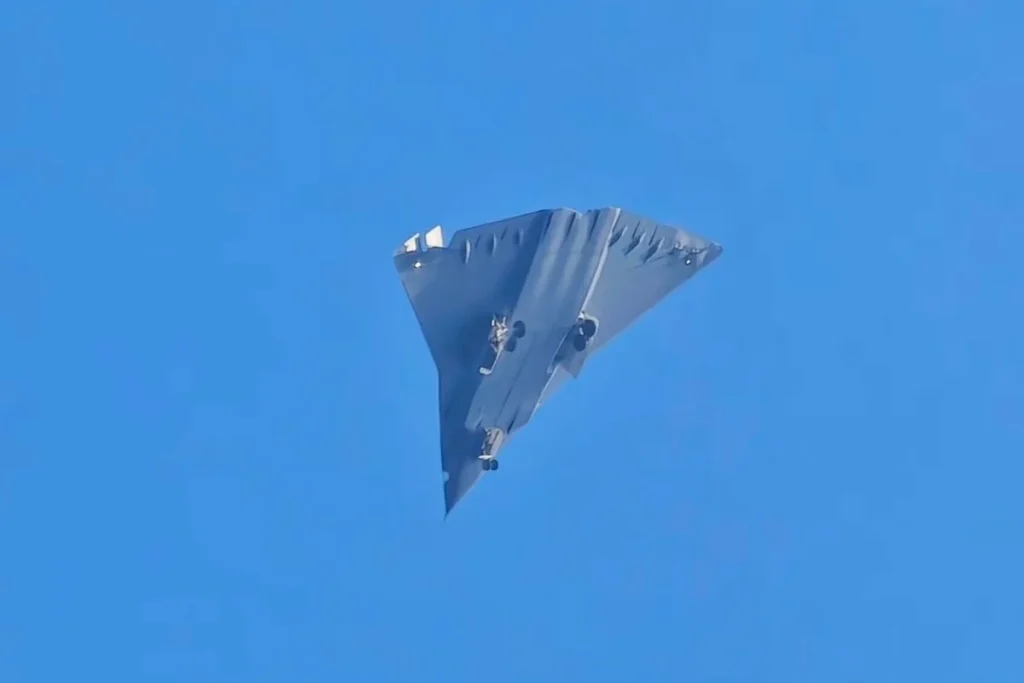

What do we know about China’s new ‘6th gen’ fighters?
Sandboxx News
-

‘Sandboxx News’ Trucker Cap
$27.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

‘AirPower’ Classic Hoodie
$46.00 – $48.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

‘AirPower’ Golf Rope Hat
$31.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

‘Sandboxx News’ Dad Hat
$27.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
